The stages of psoriasis are determined by the duration of the disease. Many psoriatists mistakenly call the stage a severe or mild form of the disease, but in medical documents this expression is used in a completely different sense.
What are the stages of psoriasis?
Psoriasis is known as a recurrent skin pathology caused by genetics. According to dermatologists, at least 2% of the world's population suffers from this disease, and this problem is very urgent. Two conditions are clearly different in psoriasis:
- Repetition.This term refers to the deterioration of the skin. In relapse, the patient experiences itching, pain, burning, excessive skin rash, irritation, and discomfort. The victim's condition is aggravated by insomnia, neurosis and anxiety.
- Remission.This word is used to improve the appearance of the skin. With remission, the skin regains its normal color, redness disappears and the area of psoriatic plaques decreases.
The stages of psoriasis partially duplicate the description of remissions and relapses, so many dermatologists use these words interchangeably. In clinical practice, 3 stages of psoriasis are described:
- progress stage;
- stationary;
- regression phase.
Given that we are talking about a cyclical process, the stages flow sequentially and form a continuous course of the disease.
fact!The developmental stage is considered the most difficult to feel.
What is psoriasis?
The progression phase is triggered by a number of triggers, such as the cold season or stress. In some cases, even an experienced dermatologist can not determine the trigger unambiguously. In the progressive stage, the following occurs:
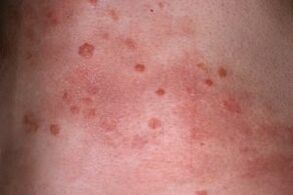
- Psoriatic nodules develop rapidly, affect the skin, and wrinkle and itch are tied together in so-called plaques. The plaque is an arbitrarily shaped spot, sometimes with uneven edges, often round or oval.
- Papules, the individual nodules of a psoriatic rash, are patches on the skin. The edges of the papules are not peeled, the central part is peeled. As a large number of dead scales accumulate, the plaques begin to rise above the surface of the skin. The swelling makes them look even more convex and uneven.
- This stage of the pathology is characterized by an isomorphic reaction, which consists of exacerbation of rashes during skin lesions, scratches, needles, cuts, microtraumas. This phenomenon is called Köbner.
Delayed reaction is characteristic of the progressive stage of psoriasis. In some cases, skin rashes appear about 9 days after exposure to a trigger (such as a food allergen). Typically, a psoriatic rash appears within 24 hours after exposure to adverse factors.
Interesting!95% of psoriasis sufferers have some form of food intolerance that can lead to relapse. To avoid aggravation, you should keep a food diary and observe the reaction to different types of food.
Stationary and recessive stages
The inpatient phase is the period of psoriasis in which the victim's condition is relatively stable. At the stationary stage:
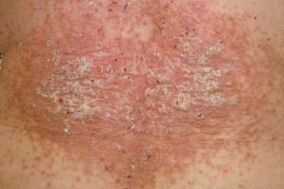
- Psoriatic plaques have a smooth contour. The entire surface of the board is covered with a thick layer of easily peeled scales. Itching and discomfort are moderate. There is no bright red inflamed edge around the papules.
- Koebner's phenomenon is not encountered with skin microtraumas, ie scratching or cutting of healthy skin no longer turns into psoriasis.
The regressive or recessive stage is characterized by massive lesions in psoriasis. At first, a false atrophic edge may appear around the papules, and then patients notice a rapid cessation of skin peeling with the formation of hyperpigmentation plaques on the site.
Pathological severity
An additional diagnostic criterion is the assessment of the area of psoriatic lesions. The term "violence" is used to describe this. Dermatologists distinguish 3 degrees of skin disease:
- is easy.Psoriatic plaques cover 1 to 3% of the total body area. The small size of the affected areas does not mean that the patient is working well. With psoriasis on the head or face, a few plaques will suffice to cause discomfort and suffering in such a person.
- Medium.The volume of psoriatic eruptions is between 3% and 10% of the total body area. It affects the back, chest and outer surfaces of the joints, scalp, palms and soles of the feet. This spread causes severe intoxication and severe pain. The patient may lose all or part of his ability to work, his mental state and nervous system deteriorate.
- It's heavy.The disease covers more than 10-15% of the skin surface. It is estimated that if psoriasis occupies more than a quarter of the total body area, the likelihood of liver or kidney failure increases significantly. Decompensated damage to internal organs can lead to the death of psoriasis.
A special scale called PASI is used to comprehensively assess the severity of psoriasis. The scales are taken into account:
- percent of healthy and sick skin;
- pathological stage;
- patients' response to drug treatment;
- individual tolerance of psoriasis (mental condition, complications from the nervous system and psyche);
- Objective data from laboratory tests in dynamics (eg, uric acid volume in a blood test).
The diagnosis takes into account all the symptoms that affect the condition of a person with psoriasis. Violence is reflected in the medical record:
- itchy skin processes;
- redness;
- swelling;
- hyperemia;
- skin thickening;
- abrasion;
- blood flow;
- swelling;
- infections;
- pain syndrome.
The extent of skin lesions on the PASI scale is described by numbers between 0 and 72, where 0 is the absence of skin symptoms and 72 is the maximum possible, maximum prevalence of the disease.
Attention!It is important for the patient to know and watch for signs of inflammation in the first place. If adverse symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a dermatologist, because psoriasis does not always enter the inpatient stage. A relapse can last for decades.
Treatment of psoriasis depends on the stage
A number of therapeutic measures have been developed for each stage of the disease, so the first thing a dermatologist does is to determine if the psoriasis is progressing, stabilizing, or declining.
How the progressive stage is treated
Every psoriasis patient predicts that remission will end with their own feelings. If the itching worsens, the skin looks worse, and if the psoriasis spreads to the surface of the body, treatment should be started. Therapy for the advanced stage has the following features:
- The patient is engaged in the prevention of further deterioration, strictly adheres to the diet, avoids the onset of the pathological process (stress, smoking, alcohol).
- Antihistamines can be used for severe itching, the added benefit of this medication is the elimination of swelling in psoriatic plaques.
- Dermatologists prescribe a wide range of topical treatments to improve, soften and thin the skin. Creams, ointments or sprays are selected by the doctor. Resin soap and solid oil compresses give positive dynamics. You can also apply a compress with Dead Sea mud or apply cosmetics.
The main task at this stage is to stop the exacerbation before the onset of long-term relapse of the disease. According to the indications, the doctor chooses corticosteroids in the form of injections or ointments.
Attention!Corticosteroids should be used in a short, intensive course under the supervision of a dermatologist. You can inject yourself or rub antihistamine ointments.
Inpatient and regressive phase therapy
The dermatologist's next steps depend on the body's response to the chosen treatment. The following scenarios are possible:
- The drug has a positive effect. Within 1-2 weeks, psoriasis goes through an inpatient phase, regression and remission occur.
- Medications have no effect. If the results are not yet visible 2-4 weeks after prescribing the course of medication, this is either a list of medications or a reason to change the attending physician.
- The drug aggravates. Such dynamics are possible, especially if the dose or frequency of application is insufficient. Relapse is delayed, psoriatic plaques cover a large part of the body, the person needs to be hospitalized.
In a medical institution, more powerful therapies are used, such as blood purification. With a favorable reaction, psoriasis enters a stationary stage that can last from a few days to several months.
Interesting!More than 80% of patients experience seasonal flare-ups. This makes the disease predictable and allows you to prepare for the onset of relapse.
The list of drugs for the inpatient and regressive stages is completely the same, but the dose and frequency of administration are less than in the advanced stage.
10-15 years remission
A competent dermatologist has the following task - to choose such drugs and physiotherapeutic substances that will give the most sustainable development of psoriasis. At the same time, the patient himself should promote treatment in all possible ways, avoid triggers and take medication responsibly. If the union between the patient and the doctor is successful, the duration of remission is not limited. Stable health can last 15 years or more.























